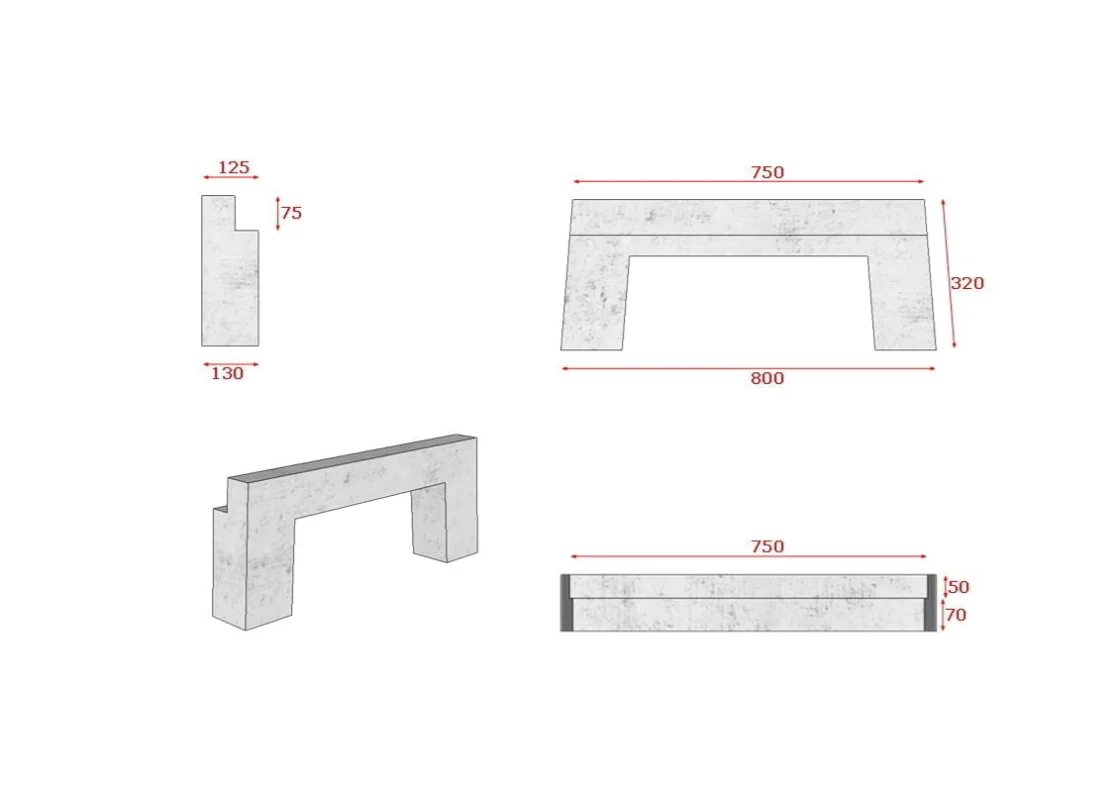
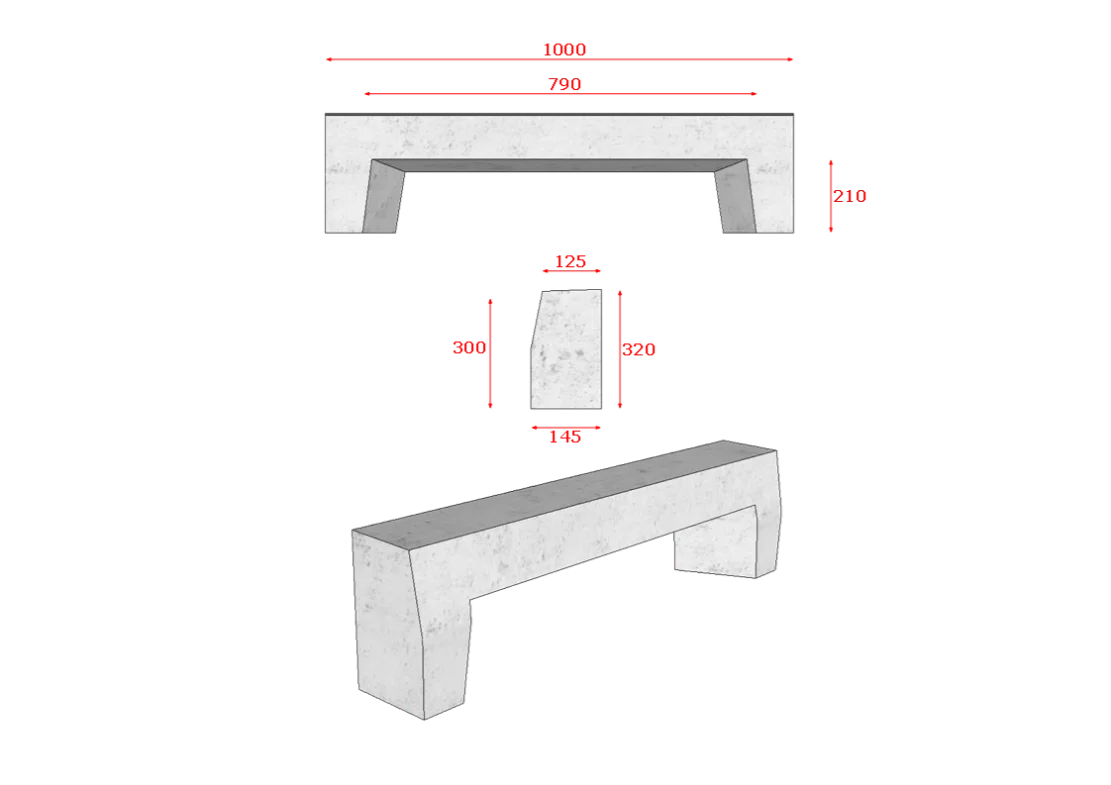
INLET KERBS
Inlet Kerbs are used along roadways and are used as point where water runs from the roads underground water pipes.
The inlet kerbs are specialized components of urban drainage systems designed to collect surface runoff from roads, pavements, and other impermeable surfaces. They are typically installed along the edge of roadways, where they direct stormwater into underground drainage networks. This helps prevent localized flooding, erosion, and water pooling that can damage infrastructure and pose safety risks.
An inlet kerb usually features an opening at the bottom or face of the kerb, allowing water to flow directly into a connected drainage pipe or catch basin. These kerbs are engineered to blend seamlessly with standard kerbing, ensuring both aesthetic integration and functional effectiveness. They are commonly made from durable materials such as precast concrete or polymer concrete to withstand heavy traffic loads and harsh weather conditions.
Design considerations for theses include hydraulic efficiency, debris capture, pedestrian safety, and ease of maintenance. Some designs incorporate grates or screens to filter out leaves, litter, and sediment, helping to reduce blockages and improve water quality. Others are shaped to accommodate wheelchair ramps or cycle lanes without obstructing accessibility.
The correct placement and sizing of inlet kerbs are critical for optimal performance. Engineers must consider factors such as rainfall intensity, road gradient, and surface area when designing stormwater systems. Well-positioned inlet kerbs can significantly reduce runoff velocity and volume, contributing to sustainable urban drainage solutions.
In summary, they play a vital role in managing stormwater in built environments. By facilitating efficient water collection and reducing surface flooding, they protect infrastructure, enhance road safety, and support environmentally responsible urban development.